Experiential Leaning: Understanding the What, Why, and How for Enriched Knowledge
- Teachers
- February 23, 2024
- Saloni Sacheti

I hear and I forget, I see and I remember, I do and I understand. ~ Confucius, 450 BC
These timeless words lie at the heart of experiential learning, a concept that is gaining prominence following the emphasis on ‘learning by doing’ in the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. As an educator, you’ve likely encountered this phrase reflecting the essence of experiential learning.
Let’s explore the enriching realm of ‘Experiential Learning’ in the context of modern education.
What is experiential learning?
Experiential learning is a teaching and learning methodology that emphasizes acquiring knowledge and skills through direct and practical experience. This approach to learning is grounded in the belief that students learn best when they are engaged in hands-on, real-world activities that enable them to apply classroom learning to authentic situations.
Let’s simplify it with the help of an example.
Imagine that you are learning to bake a cake. You could read a recipe, picturing the steps in your mind — the ‘hear and forget’ or ‘see and remember’ stage. However, with experiential learning, you actively dive in. You measure the ingredients, mix the batter, observe changes, and savour the aroma as it bakes. Tasting the final product not only gives you a delicious cake but a profound understanding of the baking process.
Experiential learning, in this case, involves hands-on participation, engaging multiple senses, and deeper comprehension as compared to merely reading a recipe.
Importance of experiential learning for students:
Experiential learning goes beyond memorization, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills as well as a deeper understanding of concepts. In the Indian context, where the focus has traditionally been on examinations and results, embracing experiential learning can bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. Here are its key benefits:
- Encourages active participation, transforming passive learners into active contributors
- Bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world application
- Significantly improves information retention
- Develops critical thinking skills as students encounter and solve problems in real-time
- Provides opportunities for students to explore diverse perspectives and cultures
- Cultivates adaptability, resilience, and a mindset of continuous learning – essential qualities in the evolving landscape of work and technology
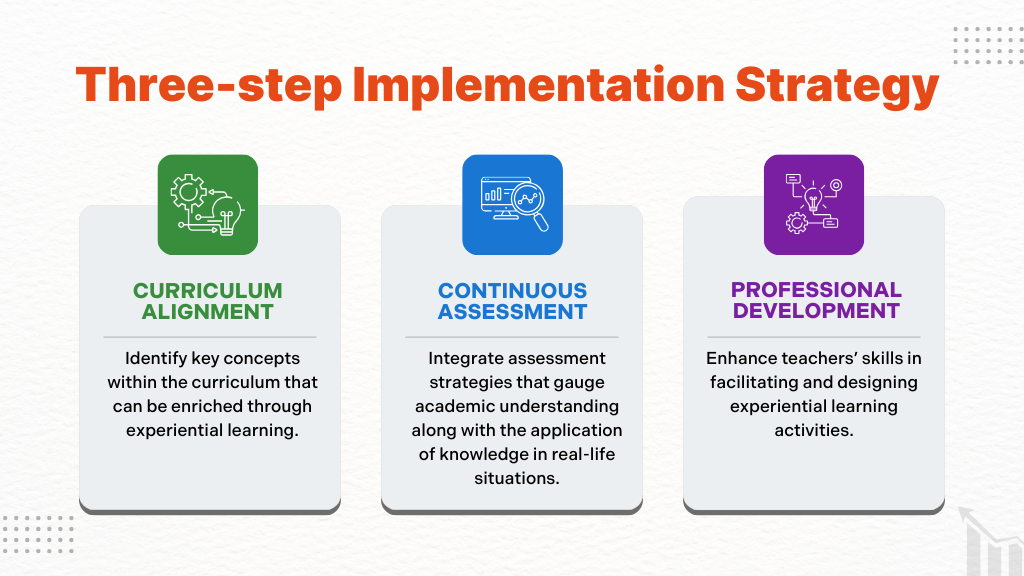
Curriculum Alignment: Identify key concepts within the curriculum that can be enriched through experiential learning. Align the activities with learning objectives to ensure seamless integration of theory and practice.
Continuous Assessment: Integrate assessment strategies that gauge academic understanding along with the application of knowledge in real-life situations. This could include project presentations, group discussions, and reflective journals.
Professional Development: Enhance teachers’ skills in facilitating and designing experiential learning activities. Taking advantage of the best practices and experiences can empower them to introduce innovative approaches in the classroom.
Approaches to implementing experiential learning:
- Project-Based Learning: Design projects that require students to investigate, analyse, and solve real-world problems. This approach encourages collaboration, critical thinking, and application of knowledge to practical situations.
- Field Trips: Take learning beyond the classroom by organizing field trips to relevant sites. Visits to museums, historical landmarks, and industry facilities can help students connect what they have learned to the real world.
- Role-Playing and Scenarios: Engage students in role-playing activities that mimic professional or real-life scenarios. This approach helps develop problem-solving skills and promotes a deeper understanding of various perspectives.
- Guest Speakers and Industry Experts: Invite guest speakers and industry experts to share their experiences and insights with students. This provides students with valuable perspectives from professionals.
- Hands-On Labs and Experiments: Incorporate hands-on experiments and laboratory activities in science and other practical subjects. This allows students to explore concepts through direct immersion and observation.
- Debates and Discussions: Organize debates and discussions on relevant topics, encouraging students to critically analyze and articulate their opinions. This approach enhances communication skills and deepens understanding through peer interaction.
- Technology Integration: Use technology to create virtual simulations, interactive lessons, and online collaborative projects. Virtual reality, augmented reality, and online platforms can provide experiential learning opportunities even in a digital environment.
In conclusion, by embracing experiential learning, educators pave the way for students to not only hear and see but most importantly, to do and understand. The shift from passive observation to active participation is not merely a pedagogical evolution; it’s a commitment to nurturing well-rounded individuals equipped with the skills and mindset to thrive in an ever-changing world.
Share On:
Written By:





